Dengue Fever Spreads Across US: The Alarming Rise of a Tropical Disease
In a startling development that has caught health officials off guard, dengue fever is rapidly expanding its reach across the United States, transforming from a rare tropical disease to a growing national health concern. The silent invasion of this mosquito-borne illness is reshaping public health strategies and raising critical questions about climate change and disease transmission.
The Unprecedented Outbreak
The numbers are unprecedented. As of June 2024, the Americas have reported more than 9.7 million dengue cases – a staggering figure that represents double the total cases from the entire previous year. The World Health Organization (WHO) has highlighted an alarming trend: an 8-fold increase in global dengue incidence between 2000 and 2019.
Who is Most at Risk?
Dengue doesn’t discriminate, but some populations are more vulnerable:
- Children ages 9-16
- Residents in southern U.S. states
- People living in areas with high mosquito populations
- Individuals with underlying health conditions
“We’re seeing a disease that was once confined to tropical regions now expanding its geographical footprint,” says Dr. Elena Rodriguez, an epidemiologist at the CDC.
Climate Change: The Hidden Catalyst
The spread of dengue is intrinsically linked to climate change. Warmer temperatures and increased rainfall create ideal breeding conditions for Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes – the primary carriers of the virus. These mosquitoes are no longer just a tropical phenomenon; they’re now regularly found in areas as far north as Washington, D.C., and the Bay Area.
Key Transmission Facts
- Virus Carriers: Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes
- Transmission: Mosquito bites
- Global Population at Risk: Approximately 4 billion people
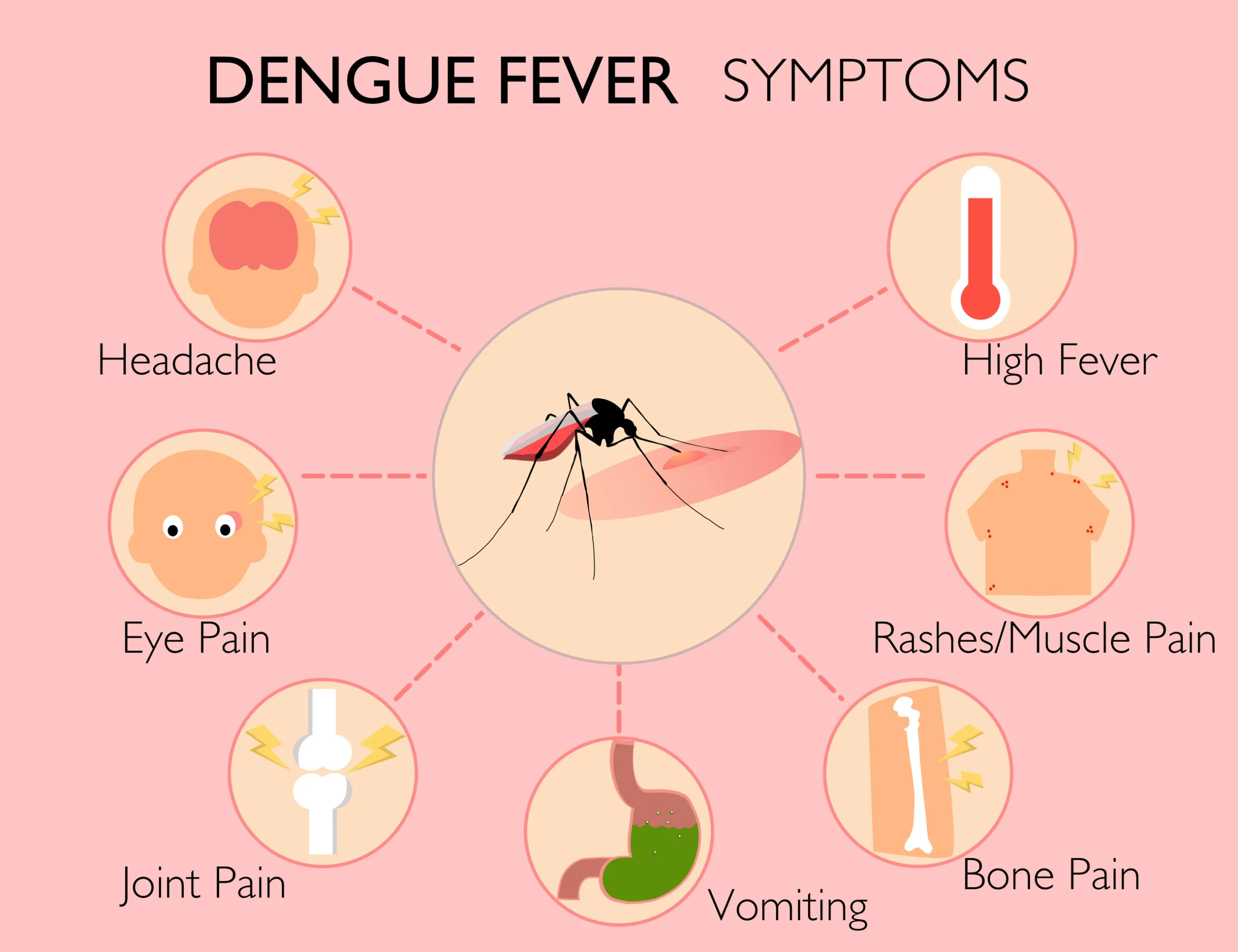
Symptoms and Prevention
While many infected individuals experience mild or no symptoms, dengue can be severe. Known colloquially as “break-bone fever” due to intense body aches, the disease can be life-threatening, especially for children, older adults, and those with compromised immune systems.
Prevention Strategies
- Use mosquito repellent
- Eliminate standing water
- Wear long-sleeved clothing
- Use mosquito nets
- Consider vaccination for eligible individuals
The Global Context
Latin America is currently experiencing its worst dengue outbreak on record, with case numbers 238% higher in the first four and a half months of 2024 compared to the previous year. The El Niño weather pattern has created exceptionally favorable conditions for mosquito proliferation.
Looking Ahead
The CDC is actively implementing strategies to address the surge, including:
- Investigating outbreaks
- Planning mosquito control programs
- Training healthcare providers
- Conducting extensive virus testing
Experts warn that this could be a preview of future health challenges, with one 2019 study predicting an additional 2 billion people will be at risk for dengue fever by 2080.
Conclusion
The rise of dengue fever in the United States is more than just a health statistic – it’s a complex interplay of climate change, global travel, and ecological transformation. As we continue to adapt to these changing conditions, prevention, awareness, and proactive healthcare will be our most powerful tools.
Stay informed, stay protected.
Note to Readers: Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized medical advice and stay updated with local health department guidelines.





Leave a Comment